THE ARCHAEOLOGICAL SITE OF AMPHIPOLIS.
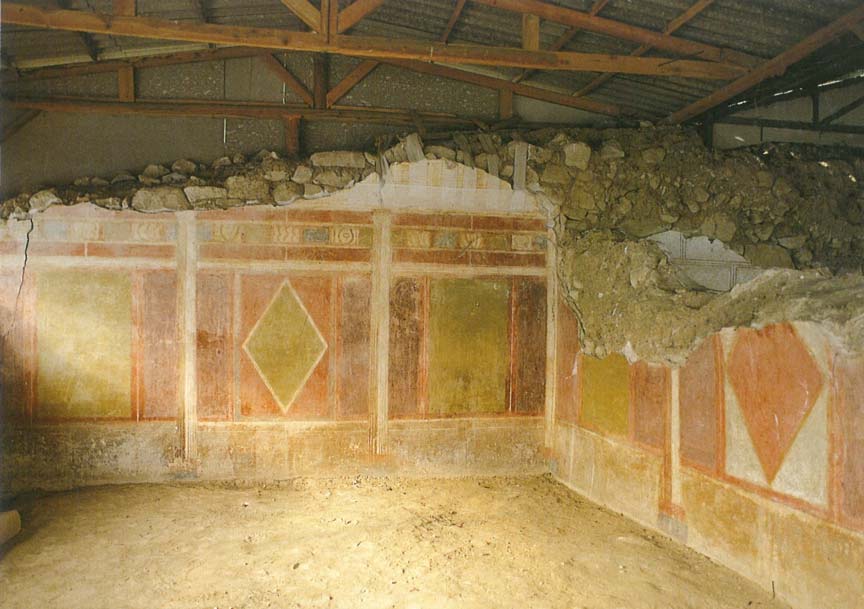
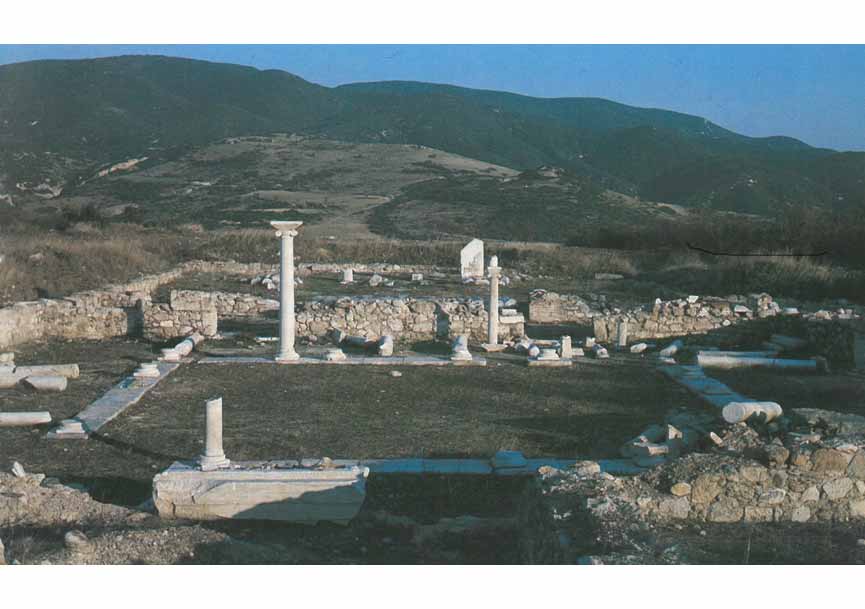
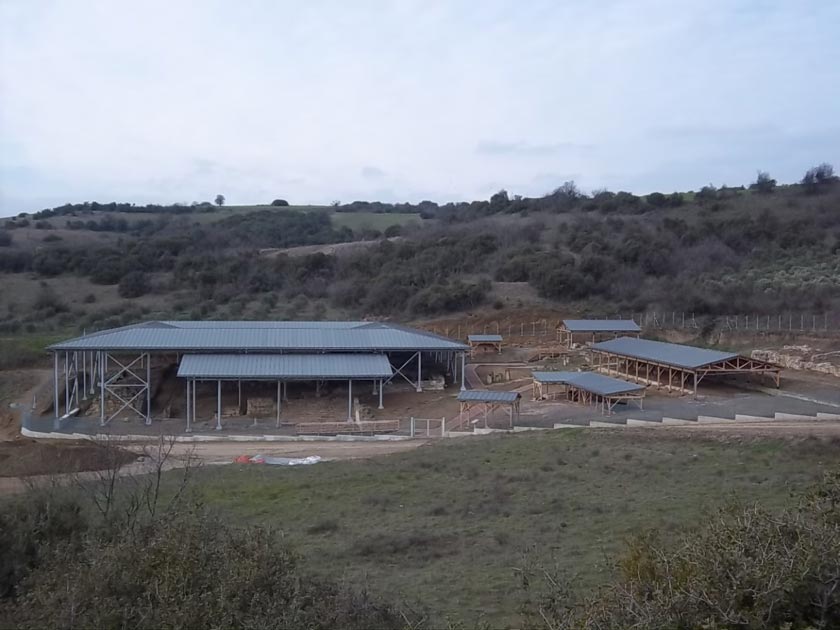
The archaeological site of Amphipolis, that is, the area of the ancient homonymous city, which is surrounded by the remains of impressive ancient walls, is one of the most important archaeological sites of Northern Greece. This is due not only to the great historical significance of the ancient city, but also to the fact that architectural remains of many important monuments (Gymnasium, Hellenistic House [Fig. 1], Roman Villa, Christian Basilicas [Fig. 2], etc.) have been unearthed there, some of which are unique in Greece (ancient wooden bridge, circular byzantine church et al.). That is why the Hellenic Ministry of Culture and Sports, over time, takes care of the preservation and protection of the monuments of this very important archaeological site. In addition to the construction of an Archaeological Museum in 1995, the most recent relative projects are the construction of protective shelters in the buildings of the Gymnasium (2014) [Fig. 3] and the restoration of the Byzantine Tower of Marmari (2015).
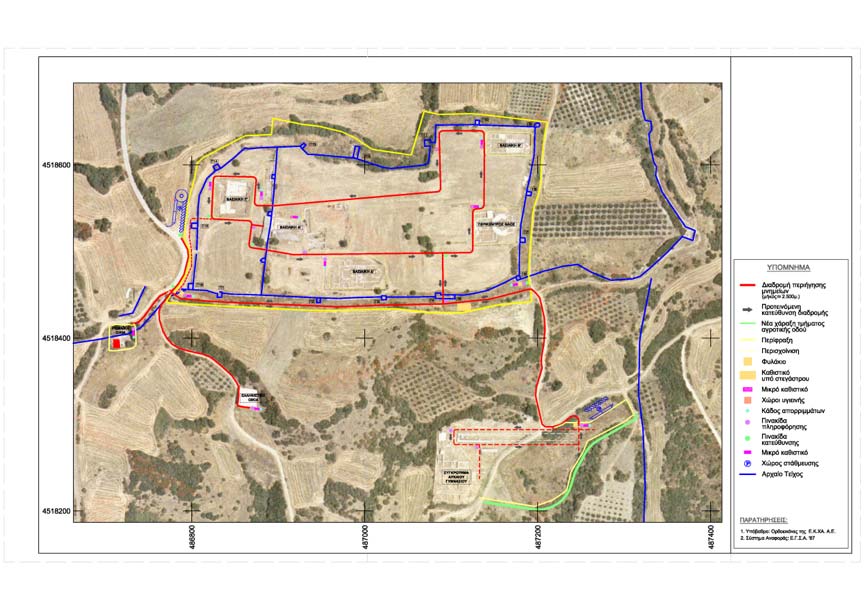
In 2017 a study entitled “Preliminary study for the management of the archaeological site of Amphipolis” was prepared by the Ministry of Culture and Sports. The study was aiming to formulate a masterplan for the site. The study, also, described in details the planning of various works for the preservation and promotion of the monuments of the site, including the works that will be carried out within the framework of the BORDERLESS CULTURE project. The objective of the aforementioned project is the creation of a network of visitors’ paths passing by most of the excavated monuments in the central area of the archaeological site of Ancient Amphipolis. More specifically, after the completion of the project, the visitors (following the paths) would have the opportunity to see up-close all the excavated monuments of the Christian Acropolis, as well as monuments in two separate sub-sections of the ancient city, southwest and southeast of the Acropolis [Fig. 4].